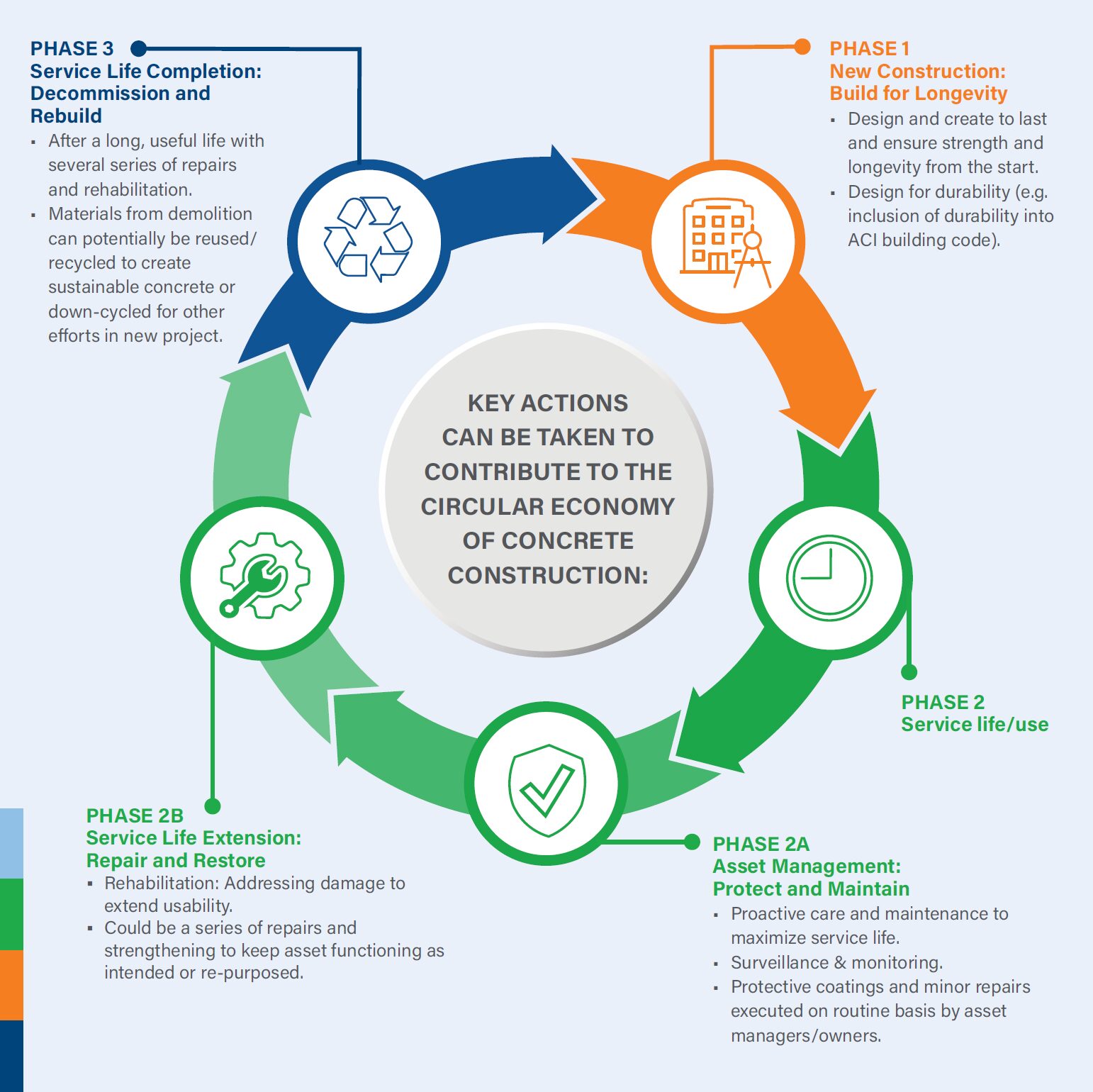
The Circular Economy of Concrete Construction
The circular economic approach to construction is a framework to prevent negative impacts of economic activity that can lead to the loss of valuable resources and damage to human health and our natural systems.
Applying circular economic principles to transform the way concrete is designed, applied, used, and maintained in construction will offer significant opportunities to reduce Green House Gas (GHG) emissions as well and other environmental impact such as depletion of natural resources, pollution of air, land, and water, and the underutilization of assets such as buildings.
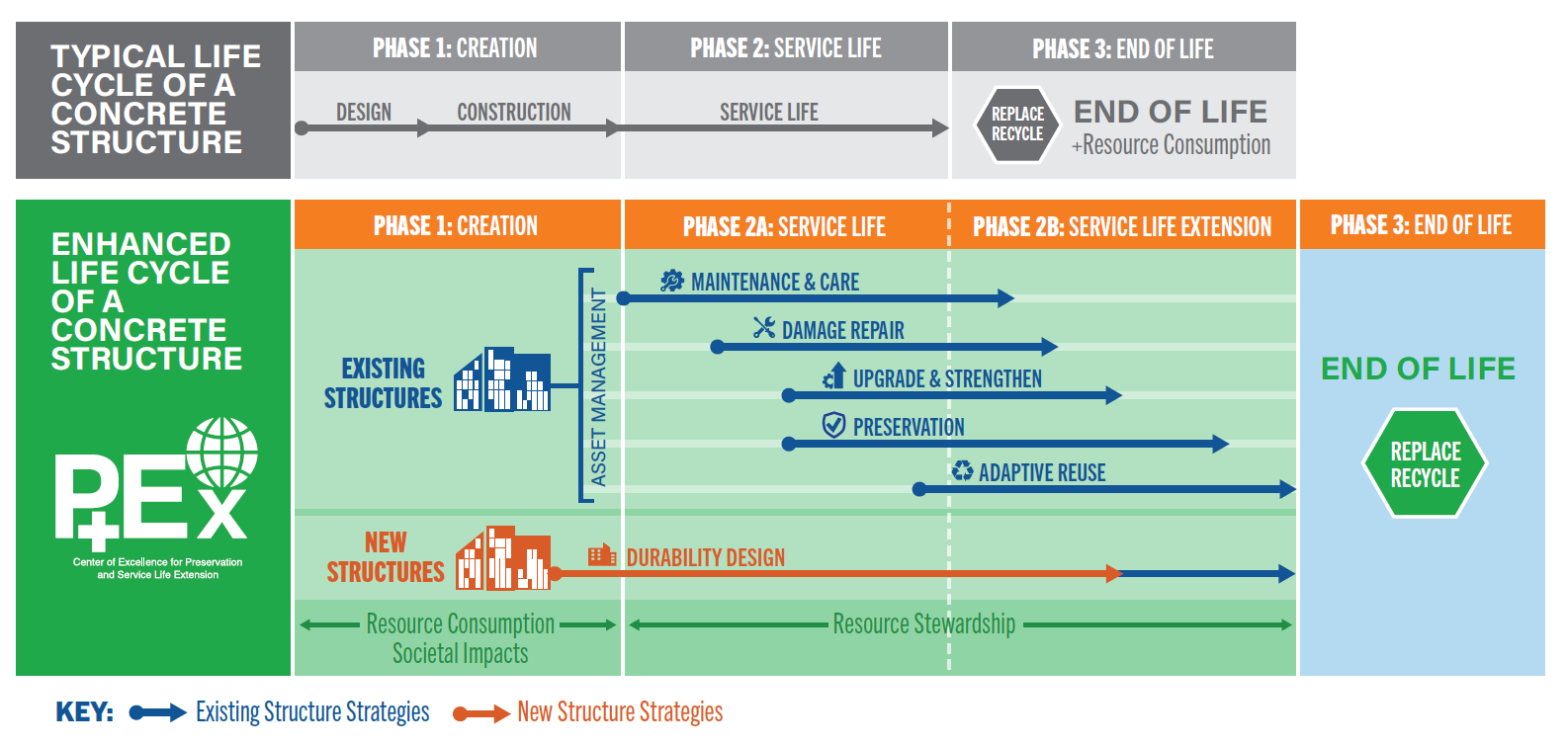
Traditionally, concrete construction focuses on the creation phase – from cradle to gate. Recent developments in decarbonization strategies have been developed by the cement and concrete industry such as GCCA 2020 to reduce GHG emissions and environmental impacts.
Still, there are enormous potentials to be captured if the full life cycle of the structure is considered. In reality, the most sustainable, low-carbon concrete structure is often the one already built. Refurbishing and retrofitting existing structures to improve energy efficiency is usually the best option for avoiding and reducing carbon emissions from the built environment.
TYPICAL AND ENHANCED LIFE CYCLE OF CONCRETE STRUCTURE
DRIVING THE CIRCULAR ECONOMY IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION